Description
Fluid flow can be categorized in several ways. Some of the most important classifications include:
Based on the Type of Particle Motion
- Laminar Flow: In laminar flow, fluid particles move in parallel layers with minimal mixing between them. This type of flow typically occurs at low velocities and in fluids with high viscosity.
- Turbulent Flow: In turbulent flow, fluid particles move randomly and chaotically, with significant mixing between layers. This type of flow usually occurs at high velocities and in fluids with low viscosity.
Change Over Time Space
- Steady Flow: In steady flow, the fluid properties at any point in space do not change over time.
- Unsteady Flow: In unsteady flow, the fluid properties at any point in space change over time.
Change in Space
- Uniform Flow: In uniform flow, the fluid properties are the same at all points in a cross-section.
- Non-uniform Flow: In non-uniform flow, the fluid properties vary at different points in a cross-section.
Laminar Flow
Laminar Flow As mentioned, in laminar flow, fluid particles move in parallel layers. Due to its simplicity, this type of flow is used in many engineering calculations and analyses.
Characteristics of Laminar Flow:
- Layered Particle Motion: Fluid particles move in thin, parallel layers, similar to sheets of paper stacked on top of each other. This layered motion results in minimal mixing between layers.
- Low Mixing Between Layers: Due to the layered motion of particles, the exchange of mass, energy, and momentum between layers is very limited. This characteristic causes the physical properties of the fluid in each layer to remain relatively constant.
- Low Velocity: Laminar flow typically occurs at low velocities. As velocity increases, the likelihood of turbulence and the transition to turbulent flow increases.
- High Viscosity: Fluids with high viscosity (such as honey or oil) are more likely to exhibit laminar flow. Viscosity is an internal force that resists deformation. In high-viscosity fluids, this force prevents turbulence.
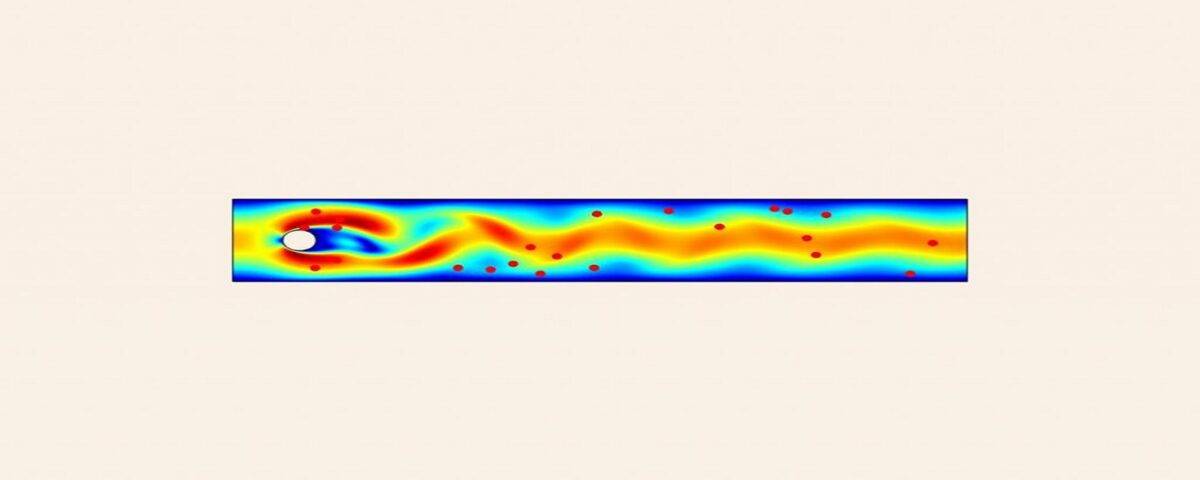
When the fluid flow passes over the bundle of pipes. Fluid energy is transferred to the pipes. The forces applied to the pipes by the fluid is one of the most important issues that exist in the category of pipes. This problem causes a lot of problems in systems that include bundles of pipes. In this project, the laminar flow around a cylinder inside the channel is simulated with the help of Comsol software.
This simulation is based on the article and has a video tutorial.