Introduction
Drying oil is an oil that turns into a solid and hard film after some time when exposed to air. Hardening of the film takes place through a chemical reaction. in which the compounds inside the film create cross-links (polymerization) through interaction with oxygen (not through evaporation of water or other solvents). Drying oils are the key ingredient in oil paints and some varnishes. Some common drying oils include linseed oil, tang oil, anemone seed oil, perilla (purple peppermint) oil, and walnut oil.
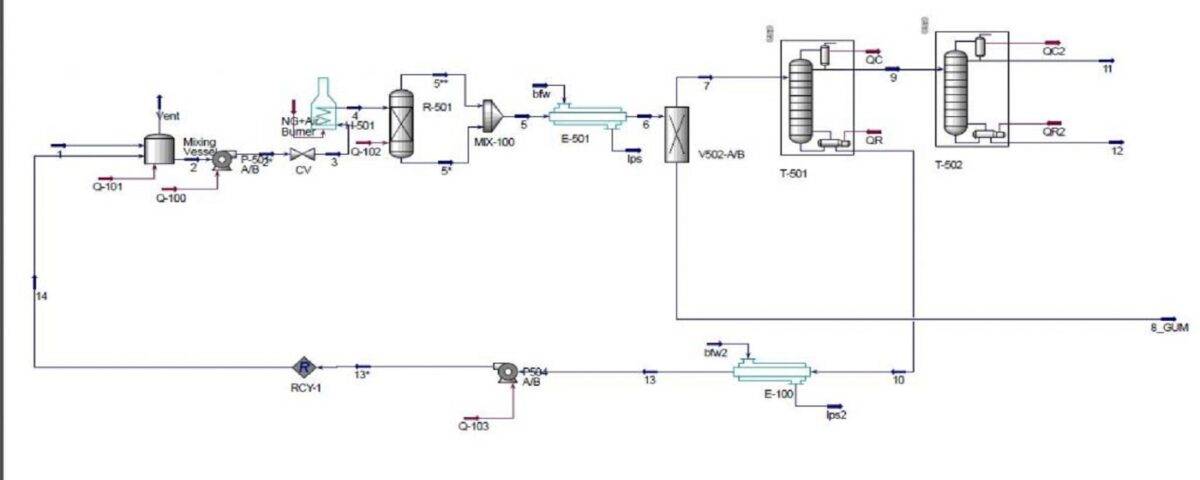
Oils are the main raw materials for making alkyd resins. In this project, the conceptual simulation of the drying oil unit has been done with the help of Aspen Hysys software.

Process Description
The conceptual simulation of the drying oil unit in Aspen HYSYS involves several stages aimed at modeling the efficiency and characteristics of the oil production process. First, the physical and chemical properties of the raw materials, including the type of oil and its components, are determined. Next, we model the input material flow, the heat and mass transfer processes, and the chemical reactions within the unit. This model includes determining the optimal temperature, pressure, and time for oil drying, as well as examining the kinetics of the relevant reactions. After setting the model parameters, the simulation results are evaluated to assess the unit’s performance, including product yield, energy consumption, and final product quality. Ultimately, this simulation can help us optimize the process and improve its performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the simulation of the drying oil process in Aspen HYSYS serves as an efficient tool for analyzing and optimizing the performance of the production unit for this type of oil. By creating precise models of the operations and chemical reactions, we can comprehensively evaluate various aspects of the process, including the effects of temperature, pressure, and time on product quality and yield. The results of this simulation not only provide valuable information for engineering and economic decision-making but also offer solutions for reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. Overall, the use of simulation in this context can lead to significant improvements in production processes, increased efficiency, and enhanced competitiveness in the market.
This simulation is designed and simulated from a book in a completely conceptual and detailed way and does not have a work report.