Introduction
Methylamines are highly important chemicals as they are commonly used as intermediates for a wide range of agrochemicals, animal feed additives, catalysts, electronics, explosives, fuel additives, and also for gas and oil treatment. The objective of this project is to design a process for converting methanol into the final products of monomethylamine (MMA), dimethylamine (DMA), and trimethylamine (TMA), while keeping the process economical, energy efficient, safe, and environmentally friendly.
Monomethylamine (MMA)
Monomethylamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3NH2. It is a colorless gas and a derivative of ammonia, but with one H atom substituted by a methyl group , It is the simplest primary amine. It is sold as a solution in methanol, ethanol, or water or as an anhydrous gas in pressurized metal containers. Methylamine is industrially sold in anhydrous form in pressurized rail tank cars and tank trailers. It has a strong fishy odor. MMA is used as a building block for the synthesis of many other commercial compounds.
Dimethylamine (DMA)
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an odor similar to ammonia. Dimethylamine is generally encountered as a solution in water with concentrations up to about 40%. Dimethylamine is a precursor to several important industrial compounds. It reacts with carbon disulfide to produce dimethyl di thiocarbamate, a precursor to a family of chemicals widely used in vulcanizing rubber. The solvents dimethylformamide and dimethylacetamide are derived from dimethylamine. It is a raw material for the production of many agricultural and pharmaceutical chemicals such as dimefox and diphenhydramine.
Trimethylamine (TMA)
Trimethylamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula N(CH3)3. This colorless, hygroscopic, and flammable tertiary amine has a strong “fishy” odor at low concentrations and an ammonia-like odor at higher concentrations. It is a gas at room temperature but is usually sold in pressurized gas cylinders or as a 40% solution in water. Trimethylamine is used in the synthesis of choline, tetramethylammonium hydroxide, plant growth regulators, strong anion exchange resins, color leveling agents, and a number of basic dyes.
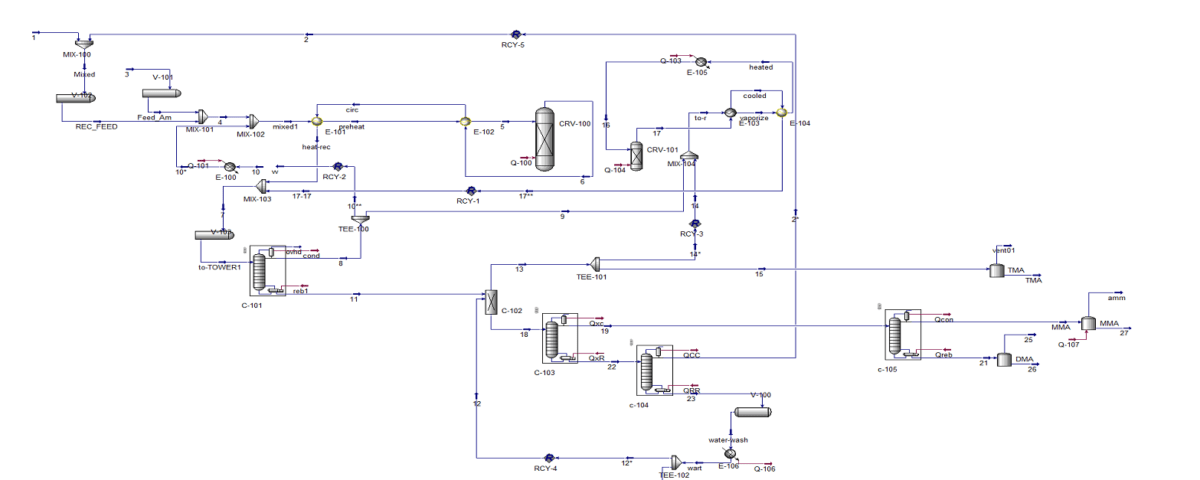
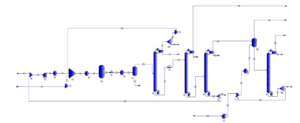
Process Description
Mixing: In the initial stage, methanol and ammonia are mixed together in precise stoichiometric ratios. The exact ratio depends on the desired type of methylamine (monomethylamine, dimethylamine, or trimethylamine).
Catalytic Reaction: The prepared mixture is then passed through a catalytic reactor. The catalyst used is typically a metal or metal oxide such as copper, nickel, or cobalt. Inside the reactor, methanol and ammonia react with each other in the presence of the catalyst, producing methylamines and water as the final products. The exothermic nature of this reaction necessitates reactor cooling to control the process temperature.
Separation: After exiting the reactor, the reaction mixture is sent to a separation unit. In this unit, methylamines are separated from water and other impurities using various methods such as distillation, liquid-liquid extraction, or evaporation.
Purification: The extracted crude methylamines may undergo additional purification processes to remove any remaining impurities. This is done using methods such as adsorption, ion exchange, or crystallization.
Conclusion
Simulations were conducted using Aspen HYSYS software. The process was subjected to measurement, cost analysis, and economic evaluation, and its profitability was determined. To enhance the base case design, the compressors, solvent, and purification were optimized along with overall thermal integration. However, the possibility of feed location optimization in distillation columns was explored.
This project was undertaken by Anil Pars Company based on a research paper.
Process Design for Producing Methylamines from Methanol and Ammonia
This project simulates the process of producing methylamines from methanol and ammonia using Aspen HYSYS version 14. A comprehensive report (PDF file) is available.