Design & Manufacture of Laboratory and Semi-Industrial Equipment
آذر ۷, ۱۴۰۳
Principles of Design Laboratory Scaffolding and Clean Room
آذر ۱۴, ۱۴۰۳Description
The steel and iron industry, as one of the largest and most energy-intensive sectors, has always faced challenges related to water scarcity and rising energy costs. Steel production processes require vast amounts of water for cooling and washing. Steam recovery in these industries not only significantly reduces water and energy consumption but also enhances industrial profitability by lowering production costs.
The growing demand for energy, especially in heavy industries like iron and steel, is a major global challenge. The iron and steel industry, being one of the most energy-intensive, accounts for a significant portion of energy consumption. Excessive energy consumption not only increases production costs but also contributes to environmental pollution and the depletion of natural resources.
The Importance of Recovering Wasted Steam in the Steel and Iron Industry Steam
as a crucial energy carrier in various industries, especially steel and iron, plays a vital role. Thermal processes and steel production generate large amounts of energy in the form of steam, which can be wasted if not managed properly. Recovering wasted steam using condensate and energy recovery systems can lead to significant reductions in energy costs.
This is particularly important for industries heavily reliant on energy, not only from an economic perspective but also from an environmental standpoint. Optimal utilization of recovered steam reduces fossil fuel consumption and consequently greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to sustainable industrial development. For instance, new hybrid systems have demonstrated up to an 88.3% reduction in water consumption, highlighting the potential of these systems to conserve valuable resources.
The Value of Water and Water and Steam Waste in Industries
1- Economic and Environmental Value of Water
Water, as a vital resource for human survival and economic growth, plays a pivotal role in sustainable development. While most industries rely on water for their production processes, water wastage in these industries can have far-reaching implications for both the economy and the environment.
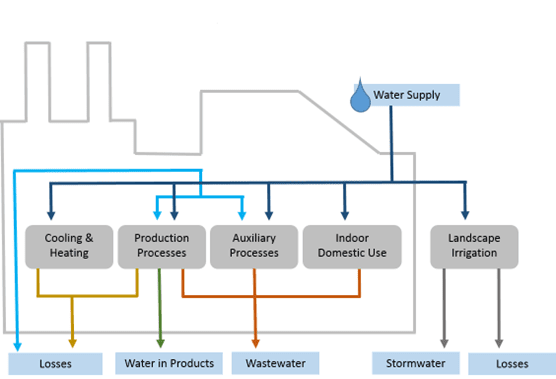
The figure below illustrates the typical water consumption in an industrial plant. In industry, water is used in a range of activities, including: production processes such as incorporation of water into the final product, washing of raw materials or final products; support processes such as preparing solvents and slurries, cleaning equipment and the environment, and removing or supplying heat; non-industrial uses such as providing sanitary needs for employees; and environmental applications such as landscaping.
Water losses can occur due to evaporation, leakage, condensation, and production and auxiliary process inefficiencies. Primary water sources typically include municipal water supplies, deep wells, and surface water bodies. However, the reuse of industrial wastewater poses unique challenges, as each production stage and process demands specific water quality.
According to reports, water consumption varies across industries, with the chemical industry consuming between 6.8% and 8.7% of total costs, and the base metals industry between 3.3% and 5.0%. These figures highlight the significant economic impact of water costs on industrial operations.
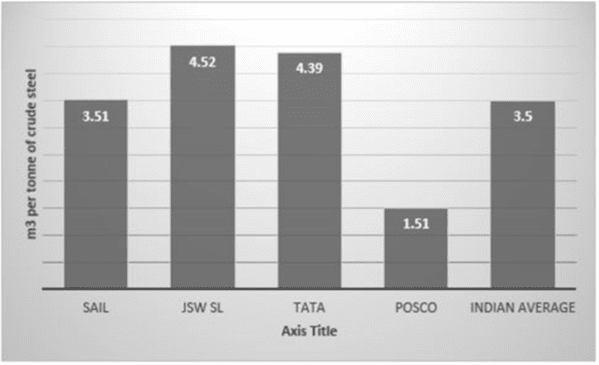
High water consumption and low recovery rates in the steel industry present significant challenges. For instance, Indian steel industries consume approximately 3.5 cubic meters of water per ton of steel produced, while advanced technologies, as exemplified by Posco, have achieved reductions to 1.5 cubic meters. This comparison underscores the potential for substantial water savings through optimized water usage technologies.
2- Water Losses and Industrial Water Usage
Water, a precious natural resource, plays a crucial role in all industrial processes. Approximately 15% of the world’s freshwater consumption is attributed to industrial production. This percentage is even higher in industrialized countries, reaching 30.7% in Europe and Central Asia. Water is utilized in every stage of the production process, including product manufacturing, washing, dilution, equipment cooling, and product transportation.
Heavy industries such as steel and iron require substantial amounts of water for their production processes. Water is extensively used in various stages, such as cooling equipment. Water wastage in these industries incurs significant costs and harms the environment. For instance, the production of one ton of steel demands thousands of liters of water. Therefore, effective water management in these industries is paramount. By employing innovative methods and advanced technologies, water consumption can be reduced, and wastage can be mitigated. This not only decreases costs but also contributes to environmental conservation.
3- Comparison of Water Consumption in Different Industries (with a Focus on Steel and Iron)
Water consumption in various industries is contingent upon the complexity of their processes and the need for temperature and heat control. Generally, petrochemical, power generation, and steel industries are among the largest water consumers. Notably, the steel and iron industries, due to their reliance on cooling systems and steam generation, exhibit exceptionally high water consumption. Compared to other industries, the production of one ton of steel requires approximately 2.66 cubic meters of water, whereas this figure is lower for chemical or refinery industries.
In the steel industry, for example, water is used for cooling molten materials, cleaning equipment, and generating steam. In these processes, water rapidly heats up, and if recovery systems are absent, water loss as steam is substantial. Conversely, in industries with lower water consumption (such as electronics or food production), water management is less critical due to lower consumption volumes.
Steel Industries and Water Consumption
Water consumption in the steel industry is influenced by various factors, including the production technologies employed and the specific processes involved. For instance, the blast furnace process, one of the most common methods in steel production, requires significant water for cooling the furnace and steel slabs during production. Reports indicate that water consumption in this process is significantly higher compared to other methods. However, in newer methods like electric arc furnaces, water consumption has been considerably reduced.
The table below compares water consumption in various industries, including the steel industry:
| Industry | Amount of water consumed per production (liters/ton) |
| Steel | 15,000 – 50,000 |
| Cement | 2,000 – 5,000 |
| Food | 1,000 – 2,500 |
| Textile |
8,000 – 12,000 |
Specific to the steel and iron industries, water wastage due to inefficient utilization and the lack of advanced technologies has become a significant challenge. Estimates suggest that water loss in these industries can account for up to 30% of total water consumption.
According to estimates, over 10% of the total water consumed in the steel industry is lost as steam, and this percentage can be even higher in older plants with less efficient technologies.
4- Environmental Challenges of Excessive Water Consumption
Excessive water consumption in industries, particularly the steel industry, not only increases operational costs but also has significant environmental impacts. Due to the high volume of water usage, steel industries have become a primary contributor to water pollution. In many countries, the discharge of untreated wastewater into rivers and natural resources is a major environmental problem. Water pollution caused by heavy metals, chemicals, and high temperatures in the steel industry can severely impact local ecosystems.
Furthermore, water wastage in these industries not only leads to the depletion of valuable natural resources but also contributes to serious social and economic problems, especially in regions facing water scarcity, such as Iran. Therefore, focusing on water consumption management and employing recovery and steam condensation technologies has become increasingly important.
Water Situation in Iran
1- Water Resources in Iran
Iran, classified as an arid and semi-arid country, grapples with severe water scarcity. The country’s surface water (rivers, lakes) and groundwater resources have significantly dwindled due to prolonged droughts, overexploitation, and climate change.
Iran experiences an annual average rainfall of only 250 millimeters, which is less than a third of the global average. Consequently, Iran is categorized as a water-scarce country, with a substantial portion of its water consumption derived from groundwater and surface runoff.
However, the distribution of water resources across the country is highly uneven. The northern regions, characterized by higher rainfall, enjoy more abundant water resources, whereas the central and eastern regions face severe water shortages.
2- Water Scarcity Crisis and the Importance of Water Conservation in Industries
According to reports from Iran’s Environmental Protection Agency, the country’s annual average rainfall has decreased to less than one-third of the global average, transforming the water resources situation into a national crisis.
In this context, large industries such as steel and iron, which have a significant demand for water for cooling and steam generation, have exerted a substantial impact on the nation’s water consumption. Due to their high water consumption, these industries are considered primary contributors to water wastage in the country.
Statistics reveal that Iran’s steel industries alone consume millions of cubic meters of water annually, with a significant portion being wasted due to inefficient usage. Therefore, optimizing water consumption in these industries and implementing water recovery technologies has emerged as a fundamental solution to mitigate Iran’s water crisis.
3- Solutions to Iran’s Water Crisis
Iran’s water scarcity crisis extends beyond its economic and environmental impacts, also leading to significant social consequences. In many regions, water shortages have forced the migration of farmers and industrialists to other areas. Additionally, social disputes over the distribution of water resources, particularly in water-scarce regions, have intensified.
A crucial strategy to address Iran’s water crisis is to invest in advanced water management technologies in industries. Implementing water recovery and reuse systems, especially in steel and iron industries, which are among the country’s largest water consumers, can significantly reduce water consumption and conserve water resources.
Furthermore, treating and reusing wastewater, as well as exploiting saline water resources and seawater desalination, can be effective solutions to reduce dependence on freshwater sources.
Cooling Water and Its Properties
Cooling water refers to a system that employs water as a medium to transfer and absorb heat. This method is extensively used in various industries, especially in heavy industries such as steel and iron, power plants, and petrochemical plants, for cooling equipment and processes. By continuously circulating through cooling systems like cooling towers, heat exchangers, and condensers, cooling water plays a crucial role in dissipating excess heat generated in industrial processes.
The Chemical and Physical Properties of Water
Water, due to its unique properties, is an ideal cooling medium in various industries. These properties include:
- High specific heat capacity: Water can absorb a significant amount of heat without a substantial increase in its temperature.
- High thermal conductivity: Water efficiently transfers heat, aiding in better temperature control.
- Low viscosity: Water flows easily through pipes, requiring less energy for pumping.
- Solvency: Water can dissolve many substances, which can be both beneficial and problematic in certain applications.
- Chemical stability: Water exhibits good stability under various industrial conditions.
The Chemical and Physical Properties of Water and Its Role in Industrial Cooling
Beyond its physical and chemical properties, cooling water plays a crucial role in reducing energy consumption and optimizing the performance of industrial equipment. In large-scale industries like steel and iron, where production processes involve high temperatures and significant energy consumption, effective temperature management is key to reducing energy consumption and increasing efficiency.
1- Reduced Energy Consumption
The high heat absorption capacity of cooling water reduces the need for other costly cooling methods. Water-based cooling systems, compared to air or oil-based systems, are more efficient at absorbing and dissipating heat quickly, thereby reducing energy consumption in cooling processes. This is particularly important in heavy industries like steel, which require continuous equipment cooling. For example, reducing the temperature of blast furnaces using cooling water decreases the fuel and energy required for heat generation.
2- Equipment Preservation and Reduced Failures
Effective cooling prolongs the lifespan of industrial equipment and reduces maintenance costs. In industries like steel and iron, where equipment is subjected to high thermal stress, cooling water prevents thermal damage and mechanical failures.
3- Optimized Industrial Processes
Cooling water also optimizes production processes. For instance, in steel production, temperature control through cooling systems improves product quality, increases production efficiency, and reduces raw material consumption.
4- Preservation of Water Resources and the Environment
In addition to reducing energy consumption, cooling water systems help conserve water resources. In closed-loop cooling systems, water circulates continuously and is returned to the process after cooling, minimizing water wastage and environmental impact.
Cooling Water Price and Costs
Costs related to cooling water supply and treatment are considered one of the most important factors in determining the operating costs of industries. A complete pricing mechanism for cooling water should include resource costs, environmental costs, and opportunity costs in order to properly determine the price of water.
-
Water Supply Costs
These costs depend on the price of water obtained from natural sources such as rivers, lakes, and wells. The cost of water supply usually varies according to geographical location and type of water source. For example, in areas where water is scarcer, the price of raw water can increase significantly. It includes the costs associated with pumping and transporting water from the source to the point of use.
-
Water Treatment Costs
Treatment equipment: To ensure that the water used in cooling systems is free of pollution and harmful substances, treatment equipment is needed. This equipment includes filters, ion exchange systems, and chemical treatments, which are expensive. The water treatment process requires energy, which adds to the operating costs.
Market Study on Water and Steam Waste in the Steel Industry
1- Analysis of Water and Steam Waste in the Steel Industry
Studies have shown that water and steam waste in the steel industry directly impacts production costs and environmental effects. Traditional cooling systems exhibit significant water consumption. Steam loss in steel industries is a prevalent issue, leading to increased production costs and reduced energy efficiency. Statistics indicate that approximately 20-30% of the steam generated in certain steel industries is wasted due to various factors such as system leaks, suboptimal recovery, and technical issues.
For instance, in Iran, the water crisis and rising energy costs have heightened the importance of steam and water recovery in industries. This is particularly significant for industries heavily reliant on water and energy resources, such as the steel and iron industry, which has substantial implications for economic and environmental efficiency.
According to the World Energy Organization, the steel and iron industries have been identified as one of the largest global water consumers in recent years. On average, between 1.5 and 6.0 cubic meters of water is required to produce one ton of steel. Furthermore, steam losses in these industries can exceed 20% of the total steam generated. This represents billions of dollars in wasted energy costs and water resources.
2- Estimation of Costs of Steam Waste in Steel and Iron Smelting Industries
Estimating the costs of water and steam waste helps identify the economic and financial impacts of these wastes. The costs of steam waste in these industries include the following:
Steam is used as a critical energy source in steelmaking processes. The cost of supplying and treating water depends on several factors, such as location, type of water source, and infrastructure required, and can vary greatly.
In the United States, public water systems that use groundwater have about 31% higher energy costs than systems that use surface water due to the need for more pumping. The energy required to treat and distribute water in municipal systems typically accounts for about 80% of the total costs.
Challenges and Issues of Steam and Water Waste in Steel and Iron Industries
Challenges of Steam Waste in Steel and Iron Industries
Steam waste in steel and iron industries is a significant issue with substantial economic and environmental impacts. Given the heavy reliance of these industries on steam as a heat source and motive force, steam losses due to inefficiencies in generation, transportation, and recovery systems lead to increased production costs and reduced efficiency. Technical and economic challenges are primary barriers to implementing steam recovery systems in steel and iron industries.
- Technical and Economic Complexities
Technical and economic complexities in steam recovery processes include challenges such as the need for advanced technologies, high costs of infrastructure and equipment, and issues arising from pressure and temperature fluctuations in the systems. Aging piping systems, due to leakage, contribute significantly to steam losses, especially in older plants. Additionally, the economic complexity arising from water pricing and regional and seasonal variations in costs makes this process more challenging. Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning and significant investments.
- Need for Advanced Technologies
To minimize steam waste, the use of advanced technologies in steam control, monitoring, and recovery is essential. Modern technologies include advanced sensors, pressure and temperature monitoring systems, and energy management software that can help reduce steam losses and optimize production processes.
However, the lack of access to these technologies in some plants, particularly in developing countries, is a major challenge. Moreover, implementing and maintaining these modern systems requires skilled and trained personnel, which many plants lack.
Introducing Iranian Steel Companies with High Steam Losses
The steel industry is one of the world’s largest consumers of water and energy resources. In Iran, several large-scale steel companies operate, not only leading in steel production but also facing significant challenges in resource management, particularly water and steam. Some of the most prominent of these companies include:
-
Esfahan Mobarakeh Steel (MSE) Co.
Mobarakeh Steel, as the largest steel producer in the automotive industry, has a production capacity of over 7 million tons per year. The company produces steel products including hot and cold rolled sheets, galvanized sheets, and other steel products. However, steel production, especially in the cooling systems sector, consumes a lot of water. According to available statistics, part of this water is wasted as steam due to the lack of efficient steam recovery systems.
-
Esfahan Steel Co.
The company is one of the largest steel ingot producers in Iran, using the Direct Reduction method to produce steel. In this process, a large amount of steam is produced and the loss of steam and water in the cooling systems is extremely high. One of the main challenges for Khuzestan Steel is the need to upgrade its cooling and steam recovery systems to reduce energy and resource waste.
Optimization of Processes in Oil, Gas and Petrochemical Industries
-
Hormozgan Steel Company
Hormozgan Steel, located in the south of the country, produces steel slabs. Given its proximity to the Persian Gulf, the company uses water resources for cooling processes. However, the company’s steam management and recovery systems also face many challenges, which increase steam and energy waste.
Steam and Water Waste in Iranian Steel Companies
Steel industries generally consume a high amount of water and energy in their production processes. A large part of this consumption is related to cooling production systems as well as steam generation in the melting and rolling processes.
In Iran, due to infrastructure problems and the lack of use of modern technologies, steam and water waste is high in many steel industries. The following is a detailed discussion of steam and water waste in various steel companies in Iran and the importance of this issue.
Esfahan Mobarakeh Steel (MSE) Co.
Esfahan Steel Company, one of the largest steel producers in Iran and the Middle East, employs hot and cold rolling processes. These processes generate significant amounts of steam. Unfortunately, due to inefficiencies in steam recovery systems, a substantial portion of this steam is vented into the atmosphere. In the hot rolling process, water is used to cool and clean hot metals, leading to substantial steam generation. The older steam recovery systems at Esfahan Steel cannot capture and reuse all the generated steam, resulting in direct atmospheric venting, leading to energy wastage and increased production costs.
Esfahan Steel Co.
As one of Iran’s oldest steel mills, Isfahan Steel Company utilizes the blast furnace process, which is highly water and energy intensive. This process demands large quantities of water for cooling and steam generation. Due to outdated equipment and inefficient recovery systems, millions of liters of water are lost as steam daily. It is estimated that this plant loses, on average, 20% of its water consumption through steam. The absence of modern steam recovery systems directly impacts production costs and maintenance expenses.
Khuzestan Steel and Hormozgan Steel
Due to their geographic locations in hot and arid regions, Khuzestan Steel and Hormozgan Steel have a high demand for cooling systems. Both companies employ the direct reduction process for steel production, which generates substantial steam. A major challenge for these companies is the high water consumption for cooling and steam generation. Cooling systems in these plants, owing to the hotter climate, require more water. Moreover, a portion of this water is lost to the atmosphere as steam without recovery. The lack of advanced steam recovery infrastructure results in the wastage of millions of liters of water and steam annually, directly impacting production costs, energy consumption, and resource utilization.
Water and Steam Losses in Iranian Steel Industries: A Quantitative Analysis
Analyses indicate that Iranian steel industries exhibit significantly higher rates of steam and water loss compared to their advanced global counterparts. Currently, many Iranian steel mills, due to the absence of modern steam recovery technologies and optimized condensate systems, face substantial energy losses. According to available data, the average steam loss in Iranian steel industries is approximately 25-30%, whereas this figure has been reduced to less than 10% in some developed countries.
This discrepancy highlights the urgent need for investment in steam recovery systems and water resource management within Iran’s steel industry. Steel production, particularly during rolling, melting, and cooling stages, demands substantial volumes of water and steam. Domestic reports suggest that in large Iranian steel companies such as Mobarakeh Steel and Esfahan Steel, an average of 15-20% of the total generated steam is wasted due to system inefficiencies. This wastage can be attributed to various factors, including:
- Lack of condensate recovery systems
- Leaks in steam equipment
- Absence of necessary standards for managing steam at high temperatures and pressures
For instance, Mobarakeh Steel Company, one of Iran’s largest steel producers, directly vents a portion of its generated steam to the atmosphere in its hot rolling lines due to the absence of advanced condensate systems. This practice increases production costs and reduces energy efficiency. Compared to international standards, this level of wastage is exceedingly high and necessitates immediate action.
Successful Companies in Steam Recovery and Preventing Water Waste
Iranian Companies with Advanced Technologies
In recent years, some of Iran’s largest steel companies have taken effective measures to address the water and energy crisis. For example:
Esfahan Mobarakeh Steel (MSE) Co.
This company is installing advanced steam recovery systems such as HRSG, which recycles steam generated in industrial processes back into the production cycle. It also uses closed-loop cooling systems to reduce the need for fresh water and prevent unnecessary water evaporation.
Khuzestan Steel
This company has significantly reduced water consumption by using air cooling (ACC) systems. It has also drastically reduced steam and energy waste by implementing Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) systems.
Esfahan Steel Co.
This company has significantly reduced water and energy consumption by installing Dry Cooling and Heat Recovery systems.
Conclusion
This project aims to investigate the feasibility of reducing steam waste in the steel and iron industries of Iran. In this study, analyses have been conducted on steam systems in these industries and various energy recovery technologies have been investigated. The project includes analyzing existing data, assessing economic and environmental impacts, and providing optimization solutions.
The use of steam recovery units is not only an environmental requirement but also a profitable investment for various industries. Given the numerous economic and environmental benefits of VRUs, companies seeking to improve their performance and reduce their costs can take a big step in this direction by utilizing the services of companies such as SANILCO.